Before the Installation of a standalone root certification authority (Standalone Root CA) the question arises as to which cryptographic algorithms should be used.
During the installation of the certificate authority, configuration parameters can be specified via a configuration file called capolicy.inf around Windows directory (usually C:\Windows).
In the CertSrv_Server category a directive AlternateSignatureAlgorithm=1 must be entered.
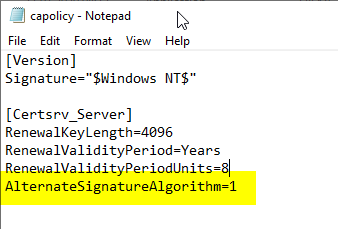
This setting first causes the own certification authority certificate to be created with PKCS#1 version 2.1 (RFC 3447) is signed. The setting will furthermore also cause that in the registration of the certification authority under...
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc\Configuration\{Common-name-of-certification authority}\CSP
...a DWORD value "AlternateSignatureAlgorithm" with content "1" is created, which in turn causes certificates issued by the certification authority to be signed with PKCS#1 version 2.1 as well.
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
Thus, the overall effect of the setting on a root Certification Authority is:
- The own Certification Authority certificate
- Certificates issued by the Certification Authority
- Revocation lists issued by the Certification Authority
In the last "official" book on Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services, "Microsoft Windows Server 2008 PKI and Certificate Security" by Brian Komar incorrectly refers to DiscreteSignatureAlgorithm, and the values were exactly reversed. At the time the book went to press, this was also correct, but with the transition from the beta version of Windows Server 2008 to the final version, the directive was renamed to "AlternateSignatureAlgorithm", including the reverse functionality. Thus, PKCS#1 was still used as the default in version 1.5 if the directive was not explicitly configured.
The installation of the certification authority can then be performed. The resulting root certificate should display the appropriate signature algorithm.
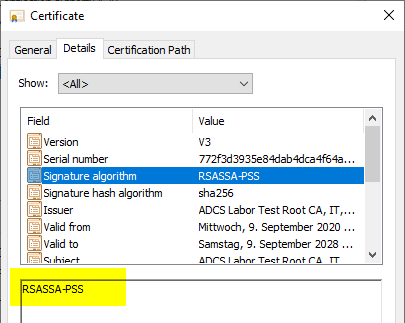
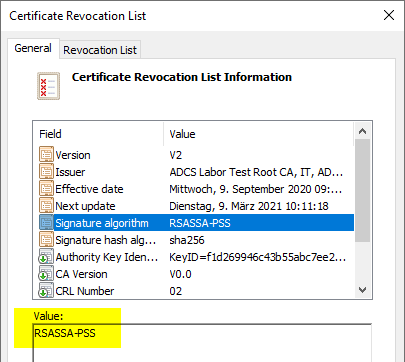
The same applies to certificates and revocation lists issued by the certification authority.
One thought on “PKCS#1 Version 2.1 für eine Stammzertifizierungsstelle (Root CA) einsetzen (eigenes und ausgestellte Zertifikate)”
Comments are closed.