When S/MIME certificates are issued, they usually contain a certificate extension "S/MIME Capabilities". This certificate extension is specified in RFC 4262 and can be used by compatible e-mail programs to specify the symmetric algorithms supported by the recipient of an encrypted message. The sender should then choose the strongest algorithm supported by the recipient.
Among other things, the Microsoft Outlook extension is evaluated and used to determine the symmetric algorithm for an encrypted email.
The information about which algorithms the recipient supports can be provided either in the form of a signed attribute within an e-mail [RFC 8551] or as a certificate extension [RFC 4262] are present. In the following the case of the certificate attribute is considered.
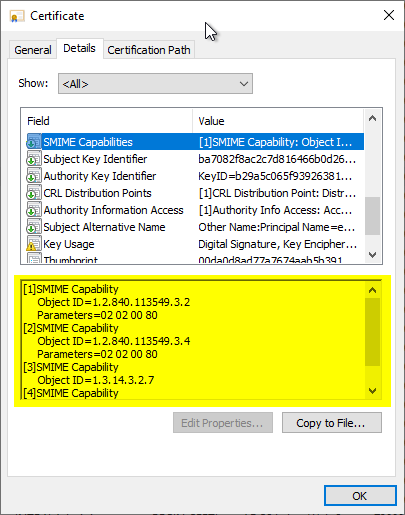
The S/MIME Capabilities attribute, defined in RFC 3851 [RFC3851], is defined to indicate cryptographic capabilities of the sender of a signed S/MIME message. This information can be used by the recipient in subsequent S/MIME secured exchanges to select appropriate cryptographic properties.
RFC 4262
However, S/MIME does involve also the scenario where, for example, a sender of an encrypted message has no prior established knowledge of the recipient's cryptographic capabilities through recent S/MIME exchanges.
In such a case, the sender is forced to rely on out-of-band means or its default configuration to select a content encryption algorithm for encrypted messages to recipients with unknown capabilities. Such default configuration may, however, be incompatible with the recipient's capabilities and/or security policy.
The solution defined in this specification leverages the fact that S/MIME encryption requires possession of the recipient's public key certificate. This certificate already contains information about the recipient's public key and the cryptographic capabilities of this key. Through the extension mechanism defined in this specification, the certificate may also identify the subject's cryptographic S/MIME capabilities. This may then be used as an optional information resource to select appropriate encryption settings for the communication.
Applications using the S/MIME Capabilities extension SHOULD NOT use information in the extension if more reliable and relevant authenticated capabilities information is available to the application.
Default values
Please note that these default values are used only in the case when the certificate request does not include a corresponding "S/MIME Capabilities" certificate extension and both the certificate authority and the certificate template are configured to include the extension. The default values depend on the type of request and are described in more detail in the article "Extend the "S/MIME Capabilities" certificate extension in issued certificates to include the Cryptography Next Generation (CNG) algorithms." described.
Change default values on the certification authority
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
On a Microsoft Certificate Authority, the default values are stored in the following registry key:
HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Service\CertSvc\Configuration\{name-of-certification authority}\PolicyModules\CertificateAuthority_MicrosoftDefault.Policy\DefaultSMIME
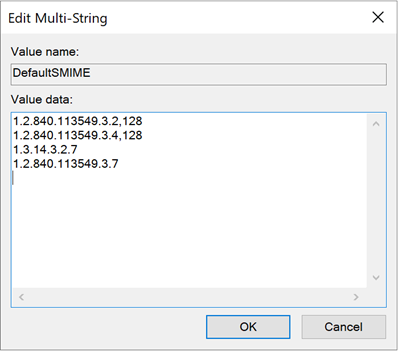
The following values are eligible for application or entry into the registry:
Possible encryption algorithms
| Name | OID | Description |
|---|---|---|
| XCN_OID_OIWSEC_of theCBC | 1.3.14.3.2.7 | Data Encryption Standard (DES) in Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) mode. Key length 56 bit. |
| XCN_OID_RSA_DES_EDE3_CBC | 1.2.840.113549.3.7 | Triple DES (3DES) in CBC mode. Key length 168 bit |
| XCN_OID_RSA_RC2CBC | 1.2.840.113549.3.2 | RC2 algorithm in CBC mode Key length between 40 and 128 bits. |
| XCN_OID_RSA_RC4 | 1.2.840.113549.3.4 | RC4 algorithm Key length between 40 and 128 bits. |
| XCN_OID_RSA_SMIMEalgCMS3DESwrap | 1.2.840.113549.1.9.16.3.6 | 3DES for key encryption Key length 168 bit |
| XCN_OID_RSA_SMIMEalgCMSRC2wrap | 1.2.840.113549.1.9.16.3.7 | RC2 for key encryption Key length 128 bit |
| XCN_OID_NIST_AES128_CBC | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.1.2 | Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in CBC mode Key length 128 bit |
| XCN_OID_NIST_AES192_CBC | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.1.22 | Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in CBC mode Key length 192 bit |
| XCN_OID_NIST_AES256_CBC | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.1.42 | Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in CBC mode Key length 256 bit |
| XCN_OID_NIST_AES128_WRAP | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.1.5 | AES for key encryption Key length 128 bit |
| XCN_OID_NIST_AES192_WRAP | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.1.25 | AES for key encryption Key length 192 bit |
| XCN_OID_NIST_AES256_WRAP | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.1.45 | AES for key encryption Key length 256 bit |
Key wrapping for S/MIME is available in the RFC 6318 described.
Possible hash algorithms
| Name | OID | Description |
|---|---|---|
| md5NoSign | 1.2.840.113549.2.5 | MD5 signature algorithm |
| sha1NoSign | 1.3.14.3.2.26 | SHA1 signature algorithm |
| sha256NoSign | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.2.1 | SHA2 signature algorithm with 256 bit key length |
| sha384NoSign | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.2.2 | SHA2 signature algorithm with 384 bit key length |
| sha512NoSign | 2.16.840.1.101.3.4.2.3 | SHA2 signature algorithm with 512 bit key length |
Removing the extension from issued certificates
The extension can also be removed from the issued certificates if required.
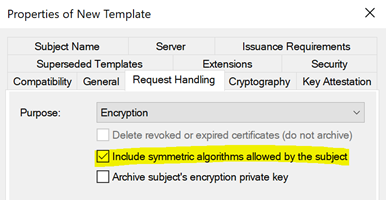
Remove via the certificate template configuration
The extension is controlled by the "Include symmetric algorithms allowed by the subject" option in the Request Handling tab of the certificate template.
Remove via the certification authority configuration
In this case, it is important to remember that the settings from the policy section of the registry are included in a backup and will also be restored in the event of a restore or migration to another server.
certutil -setreg policy\DisableExtensionList +1.2.840.113549.1.9.15
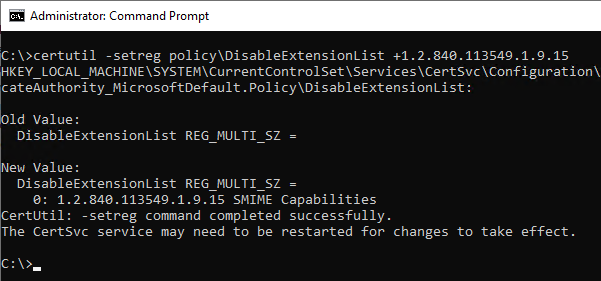
The Certification Authority service must then be restarted for the changes to be applied.
Related links:
External sources:
- X.509 Certificate Extension for Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) Capabilities (Internet Engineering Task Force)
- Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) Version 4.0 Message Specification (Internet Engineering Task Force)
- Suite B in Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) (Internet Engineering Task Force)
- Optional: Configuring Additional CA Settings and Modules (Microsoft)
- S/MIME for message signing and encryption (Microsoft)
- IX509ExtensionSmimeCapabilities interface (certenroll.h) (Microsoft)
- Hash Algorithm OID (Microsoft)
- S/MIME for message signing and encryption in Exchange Online (Microsoft)
- Secure Mail (Microsoft)
6 thoughts on “Die „S/MIME Capabilities“ Zertifikaterweiterung”
Comments are closed.