The following describes how to restore a certification authority from backup. In addition to the disaster case, this procedure is also part of the Migration of a certification authority to a new server.
Overview
The recovery of a certification authority is divided into the following substeps, which must be processed exactly in the specified order:
- Restore the certification authority certificate, either with software key or with Hardware Security Module (HSM)
- Installing the certificate authority role on the target server
- The Putting the certification authority into maintenance mode
- Restore the registry of the certification authority
- Restore the certification authority database
- Restore the delta between backup and failure
- Optional: Compacting (defragmenting) the certification authority database
- Optional: Removing old certification authority certificates from the configuration of a certification authority
- Perform function test
- Take the certification authority out of maintenance mode
Implementation
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
Restore the certification authority certificate
Restoring the certificate authority certificate differs depending on whether a hardware security module is used or not, and is described in the following two articles:
- Restoration of a Certification Authority Certificate with Hardware Security Module (HSM)
- Restoration of a certification authority certificate with software key
If the intention is to remove old certification authority certificates from the certification authority configuration at a later date, these do not have to be imported. The certification authority certificates that are to be actively used later are sufficient.
Installing the certificate authority role on the target server
Once the certification authority certificates with the private keys have been installed on the target server, the certification authority role is installed. The decisive difference to the installation of a new certification authority is that in this case no new key pair is generated, but the existing one continues to be used.
The certification authority is online again immediately after installation, populated with the configured certificate templates and accepts certificate requests. However, since the configuration of the certification authority and the certification authority database are still missing, there is a great risk that "incorrect" certificates will be issued. For this reason, it is essential that maintenance mode is activated on the certification authority immediately after the following step in order to prevent requests from requesters until the recovery and functional test is complete.
Since Windows Server 2008, the installation of the Certification Authority role consists of two steps:
- Installing the role files. This step is described in this article described.
- Configuration of the certification authority role. This step is described below.
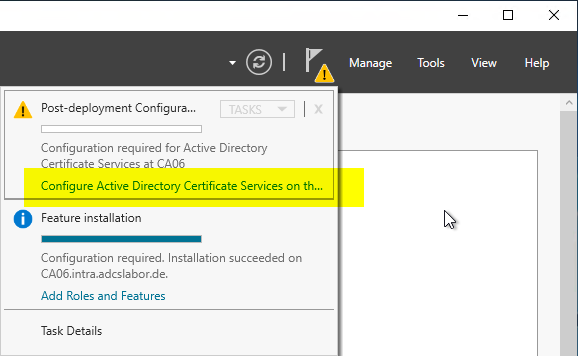
After the certificate authority role has been installed, the role configuration can be started via the Server Manager. In the upper right corner you should see an exclamation mark, via the option "Configure Active Directory Certificate Services..." the role configuration wizard can be started.
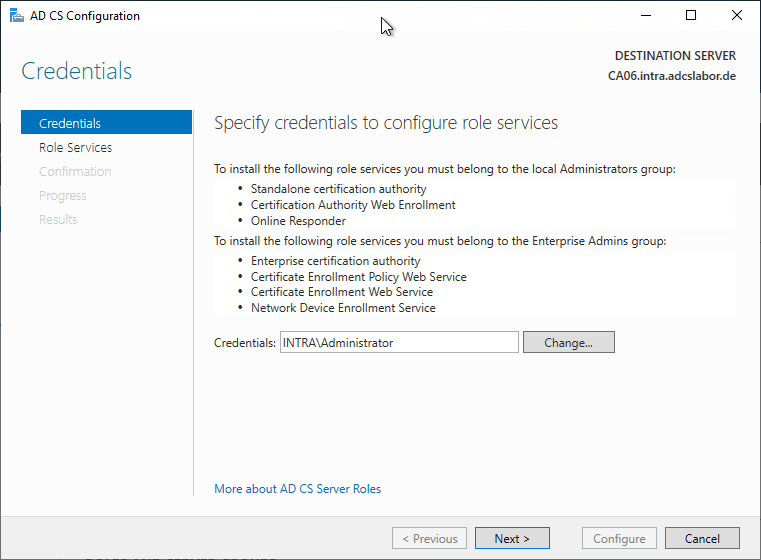
In the following dialog, the login data of the user account is specified, with which the role configuration is performed. The user account must be a member of the "Enterprise Administrators" group or must have the corresponding Delegated authorizations dispose
It is recommended that one logs in interactively (i.e. directly at the console or via Remote Desktop) with the account intended for the installation of the certification authority and does not make any changes in this dialog. Selecting a different user account may lead to unforeseen interactions (for example, in connection with Gemalto / SafeNet HSMs, the account must also be entitled to the partition).
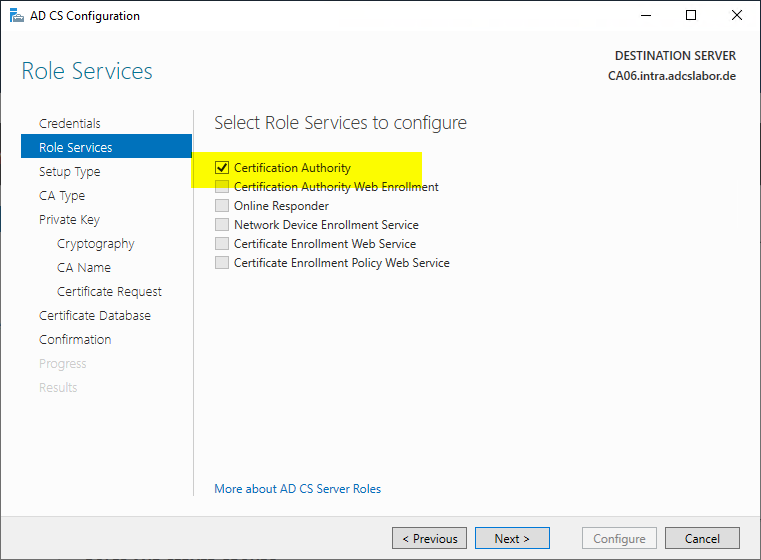
In the next dialog, the "Certification Authority" option is selected.
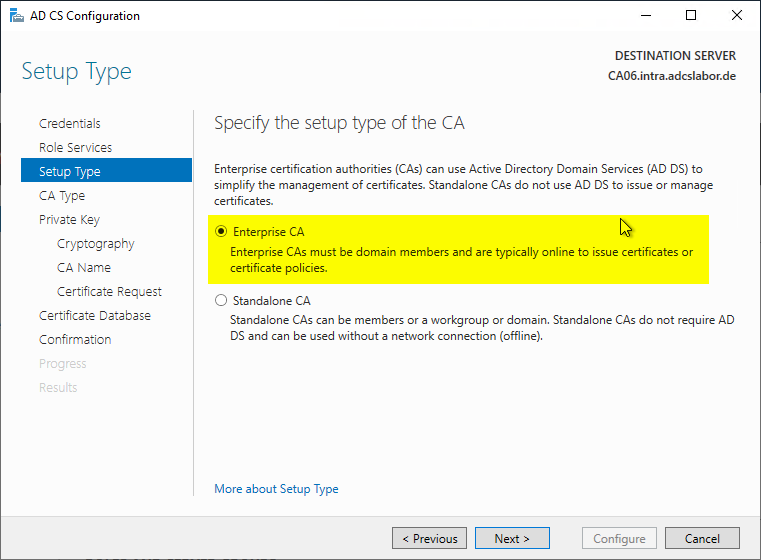
Depending on the certificate authority type, "Enterprise CA" or "Standalone CA" is selected. The following instructions describe how to restore an Active Directory integrated certificate authority, i.e. an Enterprise CA.
Depending on the certification authority type, a distinction is made between a root certification authority (Root CA) or a subordinate certification authority (Subordinate CA).
The "Subordinate CA" option includes all certification authority types that are not root certification authorities - i.e. also intermediate certification authorities.
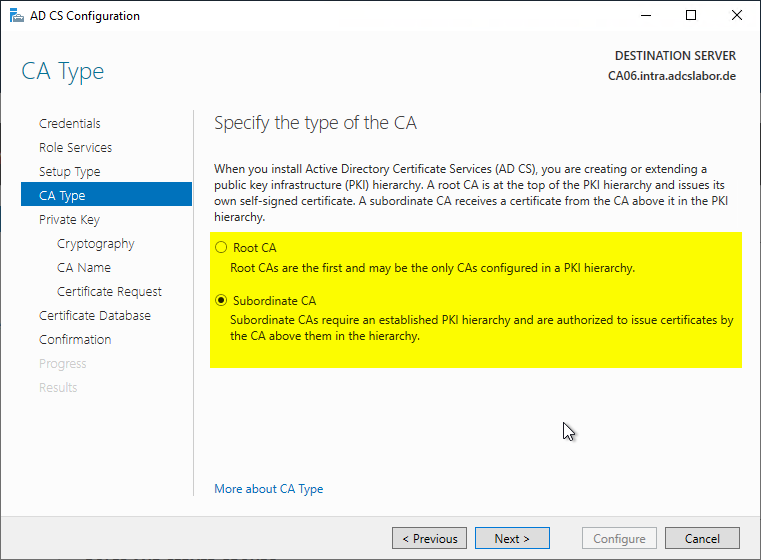
In the next dialog, an existing key pair is used instead of a new one as in a new installation. Since the certificate authority certificates were already restored before, the option "Select a certificate and use its associated private key" is selected.
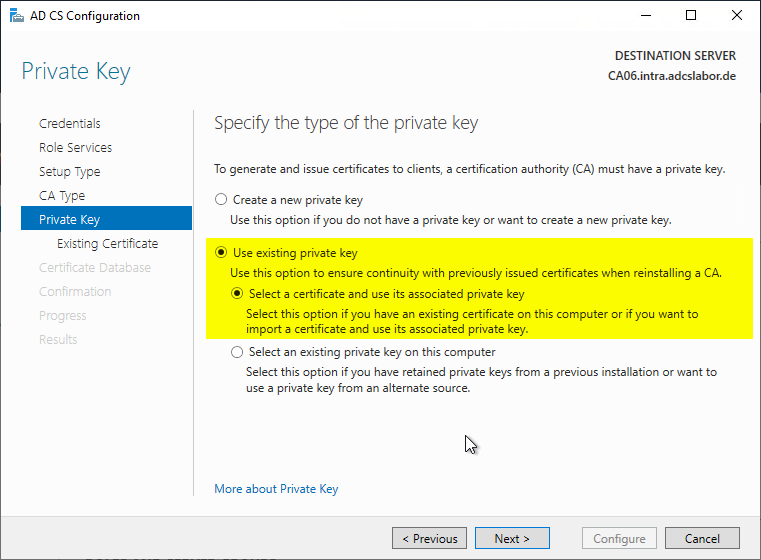
In the next dialog, the certification authority certificate is now selected. If the certification authority has several certification authority certificates, the newest one should be selected.
If the certification authority has multiple certification authority certificates, these are added back to the certification authority configuration in the subsequent step via registry recovery.
If the list of certificates is empty even though the certificate authority certificate has been correctly restored, see the article "When restoring a certification authority, the certification authority certificate is not selectable during role installation„.
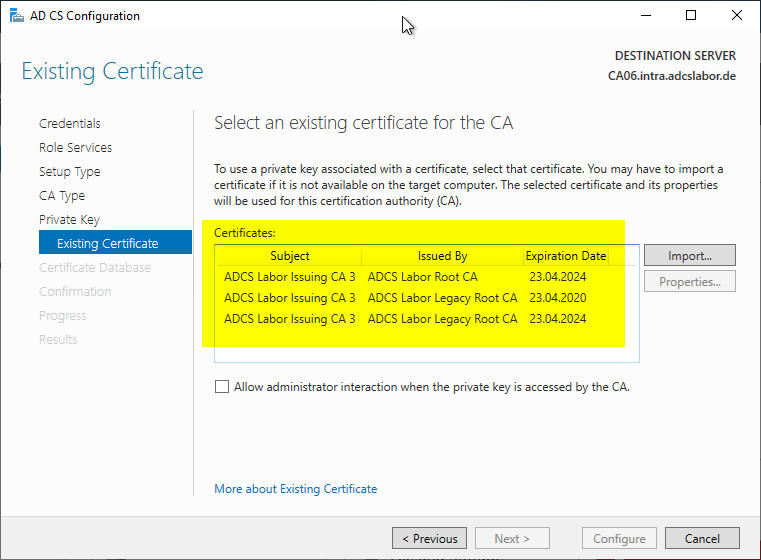
The following Windows PowerShell command can be helpful in identifying the latest certificate authority certificate:
Get-ChildItem Cert:\LocalMachine\My | Sort-Object NotBefore | Select-Object -Property Thumbprint,NotBefore,NotAfter
The following dialog is used to specify the location for the certification authority database.
The certificate authority database can later be moved to another drive or folder with little effort. The procedure is described in the article "Moving the certification authority database to another directory or drive" described.
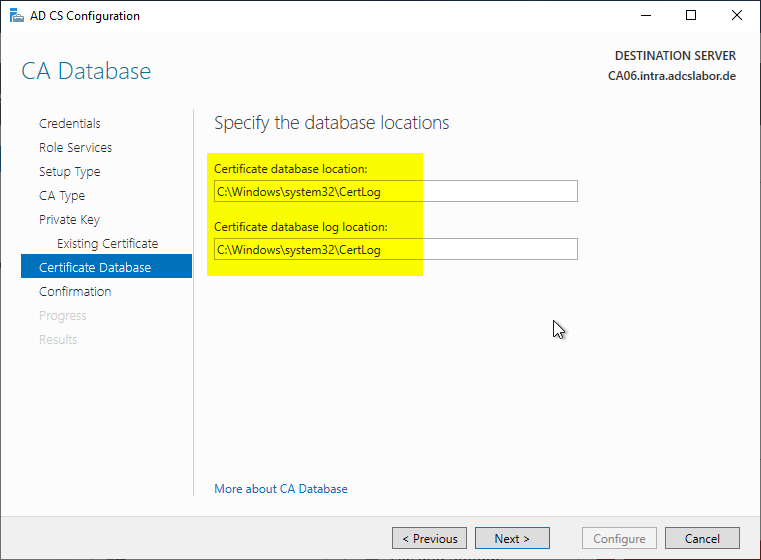
Now all relevant parameters are set and the installation of the certification authority role can be completed.
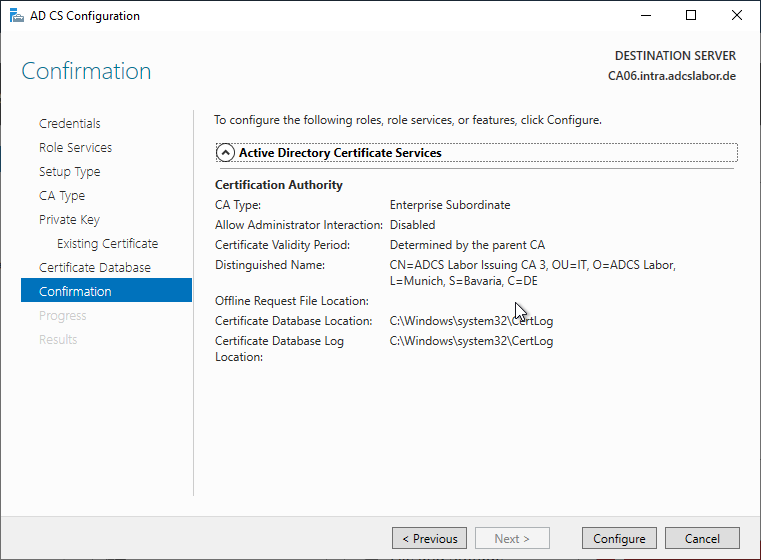
The success of the role installation is confirmed accordingly.
Putting the certification authority into maintenance mode
After the certification authority role has been installed, it is immediately available for requesting certificates and can directly issue certificates again. However, since the configuration and the certification authority database have not yet been restored, it is necessary to put the certification authority into maintenance mode. The procedure is described in the article "Putting an Active Directory integrated certification authority (Enterprise Certification Authority) into maintenance mode" described.
Restore the registry of the certification authority
The registry of the certification authority contains all settings concerning the certification authority server, among others:
- Configuration of CRL Distribution Point (CDP) and Authority Information Access (AIA) for the issued certificates
- Configuration of publication points for blacklists
- Maximum validity period for issued certificates
- Confguration of validity and Overlap periods from blacklists
- Settings regarding private key archiving (recovery agents and key generation for the Certificate Authority Exchange (CA Exchange) certificates)
- Security permissions on the certification authority
The individual configuration settings must be selected or removed manually in the registry file for the recovery. The exact procedure for importing the registry values is described in the article "Restoring the registry of a certification authority" described.
Restore the certification authority database
Before the certification authority can be put back into operation, the certification authority database must still be restored.
To do this, open the management console for the certification authority (certlm.msc) and right-click on the certification authority. In the context menu, select "All Tasks" - "Restore CA...".
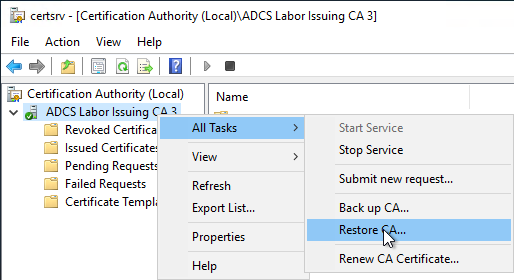
Since the certification authority service must not be started for the restoration of the certification authority, this circumstance is pointed out accordingly. Clicking on "OK" terminates the certification authority service.
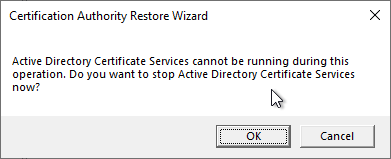
The wizard for restoring the certification authority is then opened. Clicking on "Next" takes you to the next dialog.
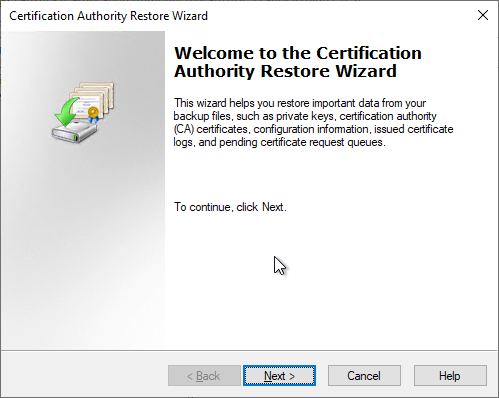
In the following dialog, the option "Certificate database and certificate database log" is selected. The certificate authority certificate including keys has already been restored, so the corresponding option is not required here. Browse" is used to select the location of the certificate authority database to be restored.
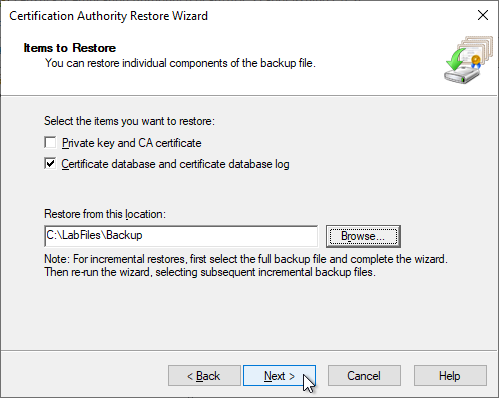
When selecting the folder, it is important that the recovery routine expects a subfolder called "DataBase". So the respective parent folder must be selected.
The wizard can now be completed.
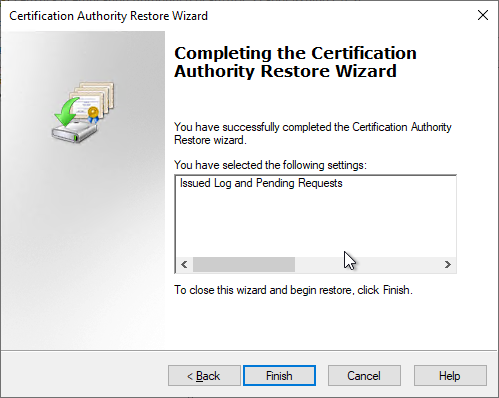
You will now be asked whether the certificate authority service should be restarted. If there are incremental backups to be restored, "No" must be selected here and the incremental backups must be restored in chronologically ascending order according to the same scheme.
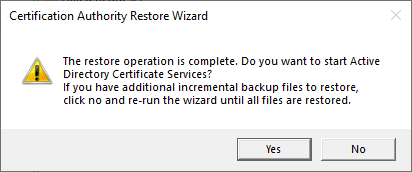
Restore the delta between backup and failure
The Certification Authority must be able to revoke certificates. For this, every (time-valid) certificate ever issued must be recorded in the certification authority database. Typically, there is a delta between the time of the last backup and the actual failure of a system.
Microsoft therefore requires that each time a certificate is issued using the SMTP Exit module a copy of each issued certificate is sent to a mailbox.
Alternative methods could include the Development of an own exit module which writes the issued certificates to a network share or uploads them against an API endpoint, for example.
The procedure for restoring the data on the SMTP exit module is described in the article "Restoring certificates from the SMTP Exit Module data" described.
Optional: compacting (defragmenting) the certification authority database
It is a good idea to compact the Certification Authority database before the Certification Authority is put back into operation. However, this only makes sense if a large number of entries from the Certification Authority database are has been deleted or is now deleted even before compactingotherwise no memory space can be gained. The procedure is described in the article "Compacting (defragmenting) the certification authority database" described.
Optional: Remove old certification authority certificates from the configuration of a certification authority
If the certification authority has been in operation for a while, there may be older certification authority certificates that have long since expired. These can be removed from the configuration of the certification authority on this occasion, so that it starts without importing the certificates.
The procedure is described in the article "Removing old certification authority certificates from the configuration of a certification authority". described.
Optional: Customize connected services
If additional services work with the certification authority and the server name has changed during the recovery, their configuration may have to be adjusted.
For the Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES), see the article "Moving Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES) to another certification authority„.
Perform function test
Before the Certification Authority is put into operation, it is essential to perform a detailed functional test to ensure that the Certification Authority is working as intended. A checklist and the procedure are described in the article "Perform functional test for a Certification Authority" to find.
Take the certification authority out of maintenance mode
After all tests are completed, the Certification Authority can exit the maintenance mode. The procedure is described in the article "Putting an Active Directory integrated certification authority (Enterprise Certification Authority) into maintenance mode“ described. Please make sure that the configuration of the certification authority and the Active Directory are in sync, otherwise no certificates can be applied for.
Related links:
- Putting an Active Directory integrated certification authority (Enterprise Certification Authority) into maintenance mode
- Compacting (defragmenting) the certification authority database
- (Mass) deletion of entries in the certification authority database (certificates, requirements, revocation lists)
- Removing old certification authority certificates from the configuration of a certification authority
- Perform functional test for a Certification Authority
- Moving the certification authority database
External sources
- AD CS Migration: Migrating the Certification Authority (Microsoft Corporation)
11 thoughts on “Wiederherstellung einer Zertifizierungsstelle aus der Sicherung (Backup)”
Comments are closed.