Implementing an Active Directory integrated certification authority often requires planning the firewall rules to be created on the network. The following is a list of the required firewall rules and any pitfalls.
Required firewall rules from clients to the certification authority
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
Go to Requesting certificates from clients via RPC/DCOM the following firewall rules are required:
| Network protocol | Destination port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 135 | RPC Endpoint Mapper |
| TCP | 49152-65535 | RPC dynamic ports |
The firewall rules are automatically configured with the installation of the certification authority role. Thus, they usually do not need to be explicitly enabled.
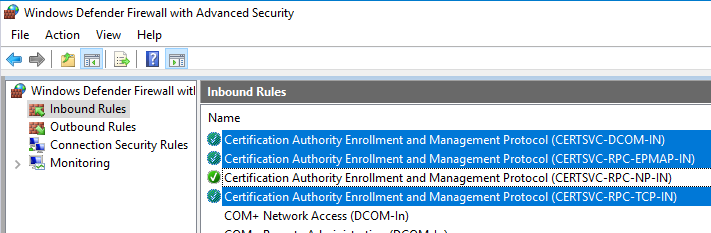
Most articles point out that TCP port 445 to the certification authority must also be opened, and a corresponding local firewall rule is also generated.
However, for the application of certificates the rule is not required. It is only needed for administrative actions. More details about this in the further course of the article.
These firewall rules are also sufficient for the Querying the certification authority database from remote systems.
Required firewall rules from clients to the revocation status validation infrastructure
All systems that apply for or verify certificates need access to the revocation status infrastructure (CRL Distribution Point, CDP and Authority Information Access, AIA).
The ports to be opened depend on the configuration of the blocking state infrastructure. If CDP and AIA are mapped via web servers, the corresponding port for the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) must be opened.
| Network protocol | Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 80 | Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) |
See also article "Required firewall rules for the online responder (OCSP)„.
If CDP and AIA are also or only provided via LDAP, the firewall ports for domain clients must be opened in the direction of the domain controllers of the forest. The firewall requirements correspond to those of a domain member.
This includes the following ports:
| Network protocol | Destination port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| TCP and UDP | 53 | Domain Name System |
| TCP | 88 | Kerberos |
| UDP | 123 | NTP |
| TCP | 135 | RPC Endpoint Mapper |
| TCP and UDP | 389 | LDAP |
| TCP | 445 | Server Message Block RPC Named Pipes |
| TCP | 636 | LDAP over SSL |
| TCP | 3268 | LDAP-GC |
| TCP | 3269 | LDAP-GC over SSL |
| TCP | 49152-65535 | RPC dynamic ports |
Required firewall rules from administrative clients to the certification authority

If the certification authority is managed from a remote computer, TCP port 445 must also be allowed in the firewall. The role configuration of NDES performs an administrative action and also requires this access at least during the configuration process. However, there is the option, NDES also install manually, in this case it is not necessary to open the firewall for TCP port 445.
| Network protocol | Destination port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 135 | RPC Endpoint Mapper |
| TCP | 49152-65535 | RPC dynamic ports |
| TCP | 445 | RPC Named Pipes |
More details on the need for TCP port 445 in conjunction with the individual ADCS roles later in the article.
Is TCP 445 required from clients to the certification authority?
In the context of hardening measures, the question may arise whether TCP port 445 from the clients to the certification authority is really necessary. The answer to this is:
It depends.
TCP port 445 is used not only for the commonly known Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, also known as Common Internet File System (CIFS), but also for RPC name pipes, as in the case of the certification authority. Some functions of the certification authority need this port to work.
Here is a list:
| Use case | Result (TCP 445 not opened) |
|---|---|
| Requesting certificates via RPC/DCOM (manual and AutoEnrollment) | Works |
| Querying the certification authority database | Works |
| NDES Role configuration | Works not |
| Requesting certificates via NDES | Works |
| Requesting certificates via Certification Authority Web Enrollment | Works |
| Certificate Enrollment of the Online Responders (OCSP, uses own enrollment code) | Works |
| Administration of the certification authority via remote server management tools | Works not |
The TCP port 445 is therefore only used for the ICertAdmin interface is required. In general, it is therefore advisable not to make this port accessible to all clients.
Both the role configuration of NDES and the remote server management tools will fail with the error message "The RPC server is unavailable. 0x800706ba (WIN32: 1722 RPC_S_SERVER_UNAVAILABLE)".if TCP port 445 is not open for the corresponding system.
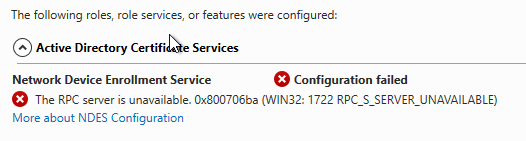
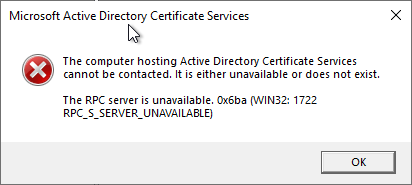
Here, however, either only temporary or fine-granular firewall rules should be used to keep the possible attack vectors as low as possible.
Required firewall rules from the certification authority to other hosts
Outbound, if it is an Active Directory-integrated certification authority, it only needs to communicate with the domain controllers of the forest. The firewall requirements correspond to those of a domain member.
This includes the following ports:
| Network protocol | Destination port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| TCP and UDP | 53 | Domain Name System |
| TCP | 88 | Kerberos |
| UDP | 123 | NTP |
| TCP | 135 | RPC Endpoint Mapper |
| TCP and UDP | 389 | LDAP |
| TCP | 445 | Server Message Block RPC Named Pipes |
| TCP | 636 | LDAP over SSL |
| TCP | 3268 | LDAP-GC |
| TCP | 3269 | LDAP-GC over SSL |
| TCP | 49152-65535 | RPC dynamic ports |
Is TCP 445 required from the certification authority to the domain controllers?
In the context of hardening measures, the question may arise whether TCP port 445 from the certification authority to the domain controllers is really necessary. The answer to this is:
Clear yes!
The Kerberos Authentication certificate template preferred for domain controllers and certificate templates derived from it contain the flag CT_FLAG_SUBJECT_ALT_REQUIRE_DOMAIN_DNS in the msPKI-Certificate-Name-Flag Attribute.
This flag causes the certification authority to enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) and the NETBIOS name of the requestor in the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) extension of the certificate and requires that the certification authority can talk to the requesting domain controller via NTLM.
This communication takes place via TCP port 445, which must be released accordingly in the firewall configuration of the network.
If the port is not accessible on the domain controller, the certificate request will fail with the error message "The RPC server is unavailable. 0x800706ba (WIN32: 1722 RPC_SERVER_UNAVAILABLE)"..
Special case of Certification Authority Web Enrollment (CAWE)
What is special about the CAWE role is that the CA will attempt to open a connection to the CAWE server's dynamic RPC ports in response to a certificate request from CAWE. If this firewall rule is not set up, the application for certificates via CAWE takes a very long time or breaks off completely.
| Network protocol | Destination port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 135 | RPC Endpoint Mapper |
| TCP | 49152-65535 | RPC dynamic ports |
See also article "Required firewall rules for Certification Authority Web Enrollment (CAWE)„.
Restore the default Windows Firewall rules on the certification authority
The default Windows Firewall rules on a certification authority can be re-enabled with the following Windows PowerShell command.
Enable-NetFirewallRule `
-Name Microsoft-Windows-CertificateServices-CertSvc-DCOM-In
Enable-NetFirewallRule `
-Name Microsoft-Windows-CertificateServices-CertSvc-RPC-EPMAP-In
Enable-NetFirewallRule `
-Name Microsoft-Windows-CertificateServices-CertSvc-RPC-NP-In
Enable-NetFirewallRule `
-Name Microsoft-Windows-CertificateServices-CertSvc-RPC-TCP-In
Enable-NetFirewallRule `
-Name Microsoft-Windows-CertificateServices-CertSvc-TCP-Out
Related links:
- Troubleshooting for automatic certificate request (autoenrollment) via RPC/DCOM
- Required firewall rules for the Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES)
- Required Firewall Rules for Certificate Enrollment Policy (CEP) Web Service
- Required firewall rules for the Certificate Enrollment Web Service (CES)
- Required firewall rules for the online responder (OCSP)
- Required firewall rules for Certification Authority Web Enrollment (CAWE)
- Service overview and network port requirements for Windows
- Requesting a certificate for domain controller fails with error message "The RPC server is unavailable. 0x800706ba (WIN32: 1722 RPC_SERVER_UNAVAILABLE)".
- Role configuration for Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES) fails with error message "The RPC server is unavailable. 0x800706ba (WIN32: 1722 RPC_S_SERVER_UNAVAILABLE)".
- Certificates for domain controllers do not contain the domain name in the Subject Alternative Name (SAN)
21 thoughts on “Benötigte Firewallregeln für Active Directory Certificate Services”
Comments are closed.