The following is a description of what configuration settings are necessary for a certificate hierarchy based on Active Directory Certificate Services to be compliant with the "Common PKI" standard.
The "Common PKI" standard is described as follows.
The Common PKI specification is a profile of internationally used and recognized standards for electronic signatures, encryption and public key infrastructures. The Common PKI takes into account all business-relevant electronic signatures up to the qualified electronic signature according to the German Signature Act (SigG), which can be used to comply with the formal requirements in private and administrative law. The specification also includes security functionalities for secure e-mail with different security levels and compatibility with internationally accepted standards. This enables the rapid availability of interoperable security products both at the certification service provider level and at the user level (client side).
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Common_PKI
Overview
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
The following configuration requirements for Microsoft certification authorities are derived from the Common PKI:
- The "Key Usage" extension of the certification authority certificates must not include the "DigitalSignature" key usage (see also RFC 5280).
- The "Key Usage" extension of each certificate in the hierarchy must be marked as critical.
- The Subject Distinguished Name of each certificate in the hierarchy should be be encoded in UTF-8 instead of Unicode to allow the use of special characters such as Umlauts to enable. This is the default setting of the Microsoft Certification Authority since at least Windows Server 2012 R2.
Strings MAY be encoded as PrintableString in order to ensure a better interoperability with legacy applications. If a string cannot be represented in the PrintableString character set, UTF8String encoding MUST be used.
Common PKI Part 1 - Page 12
This extension MUST always be included in CA and end entity certificates and MUST be marked critical.
Common PKI Part 1 - Page 22
CA certificates: the keyCertSign bit MUST be set. Additionally, the crlSign bit MAY be set too, if the CA uses the corresponding key to sign CRLs too. Other bits MUST NOT be set.
If the subject public key is only to be used for verifying signatures on certificates and/or CRLs, then the digitalSignature and nonRepudiation bits SHOULD NOT be set.
RFC 5280, 4.2.1.3
The Common PKI Standard further specifies that Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs) must be no longer than 64 characters, which is the default behavior of the Microsoft Certification Authority, however could be changed.
Implementation
The implementation differs depending on the Certification Authority role:
- Special settings for root certification authorities (root CA).
- Special settings for offline certification authorities (whether root, intermediate or subordinate certification authority).
- Settings for all types of Certification Authorities.
Special settings for root certification authorities
This step must take place before the root certification authority is installed, or before the root certification authority certificate is renewed. However, a renewal of the root certification authority certificate requires that this must be communicated to all subscribers, since it technically involves the establishment of a new certification authority hierarchy.
Root Certification Authorities not only issue certificates for other Certification Authorities, but also issue their own.
In order to cause the "Key Usage" extension of the own certification authority certificate to be marked as critical and not include the "DigitalSignature" key usage, the capolicy.inf File of the root Certification Authority to be extended by the following section.
[Extensions]
2.5.29.15 = AwIBBg==
Critical = 2.5.29.15
Contrary to instructions to the contrary, it is not necessary to explicitly configure the encoding of the subject DN and issuer DN of root certificate authorities to UTF-8. This can lead to compatibility issues when verifying the certificate chain.
In general, only characters that can be encoded with ASN.1 PrintableString (effectively all representable ASCII characters) should be used for the Subject DN of a certification authority.
Special settings for offline certification authorities
Offline certification authorities do not know certificate templates, so they have to fall back on default values.
To cause the "Key Usage" extension in certificates issued by the certification authority to be marked as critical and not include the "DigitalSignature" key usage, the following command line command must be executed on each offline certification authority.
certutil -setreg policy\EditFlags -EDITF_ADDOLDKEYUSAGE
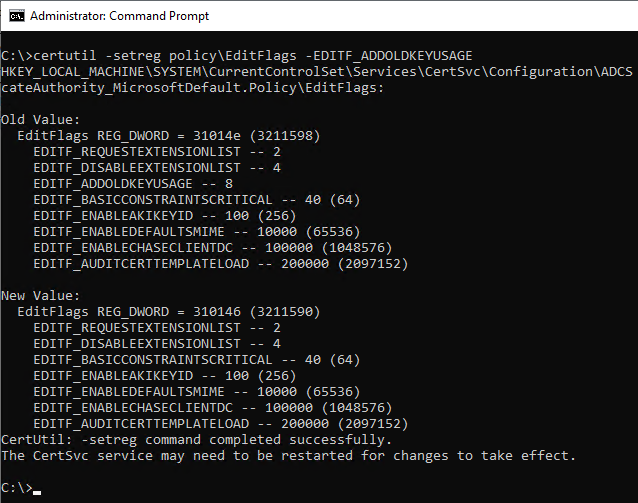
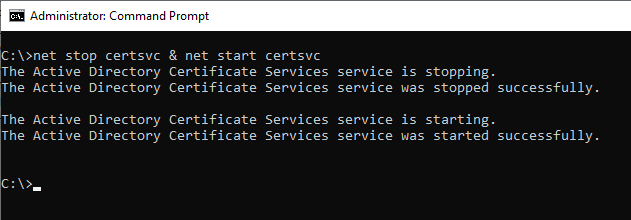
After the change, the Certification Authority service must be restarted for the changes to be applied.
Settings for all types of Certification Authorities
Contrary to the official guide from Microsoft it is not necessary and in some cases even harmful, force all Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs) in issued certificates to be encoded with UTF-8 by setting the ENUM_TELETEX_FORCEUTF8 flag. Instead, the flag ENUM_TELETEX_UTF8 (without "FORCE") should be set, which is already the case in the default setting.
Thus, RDNs that contain only ASCII characters are automatically encoded in ASN.1 PrintableString (if they already were in the submitted certificate request), which is compliant with Common PKI. If an RDN also contains other special characters, it is automatically mapped to UTF-8 in the issued certificate.
Related links:
- Removing ADCS-specific extensions from certificates
- Umlauts in certification authority certificates
- Certificate request fails with error message "Error Parsing Request The request subject name is invalid or too long. 0x80094001 (-2146877439 CERTSRV_E_BAD_REQUESTSUBJECT)".
- Basics: Configuration file for the certification authority (capolicy.inf)
- Character encoding in the Subject Distinguished Name of certificate requests and issued certificates
External sources
- Common PKI (Wikipedia)
- Common PKI Specification V2.0 (January 20th, 2009) (archive link)
- How to make a stand-alone certification authority that is running Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 or an x64-based version of Windows Server 2003 compliant with ISIS-MTT version 1.1 (Microsoft, archive link)
- Use signed policies to protect Windows Defender Application Control against tampering (Windows) - Windows security | Microsoft Docs (Microsoft)
5 thoughts on “Beschreibung der notwendigen Konfigurationseinstellungen für das „Common PKI“ Zertifikatprofil”
Comments are closed.