To use Remote Desktop certificates, it is necessary to configure an appropriate certificate template.
Rob Greene from Microsoft points out in a blog entry published in September 2024 that Remote Desktop Certificates not (as described below) are to be applied for via autoenrollment.
The remote desktop session host can create certificates with the following Extended Key Usages (EKU) use
- Server Authentication (OID: 1.3.6.1.5.7.3.1)
- Remote Desktop Authentication (OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.54.1.2)
It is recommended that the Remote Desktop Authentication EKU is used, as this ensures that the certificates are only used for this purpose and not, for example, for providing a web server as well.
Likewise, when using the "Server Authentication" EKU in combination with a Key Storage Provider (KSP) to problems with the Active Directory Web Services (ADWS) come as these do not support KSP and the certificate selection filters only on EKU and the fully qualified hostname. Such conflicts can be avoided when using Remote Desktop Authentication EKU.
However, the Remote Desktop Authentication EKU is not defined in the delivery state of the Active Directory directory service. This must be done during the configuration of the certificate template.
Certificate template configuration
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
First, a copy of the Workstation Authentication certificate template is created and edited using the Certificate Template Management Console (certtmpl.msc).
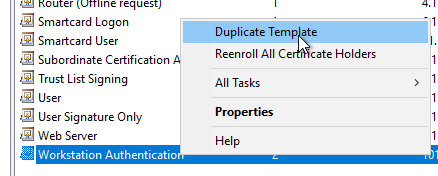
Compatibility" tab
We intend, Key Storage Provider (KSP) to be used. For this, it is necessary to set the compatibility settings for the certificate authority and certificate recipient to "Windows Vista" or "Windows Server 2008".
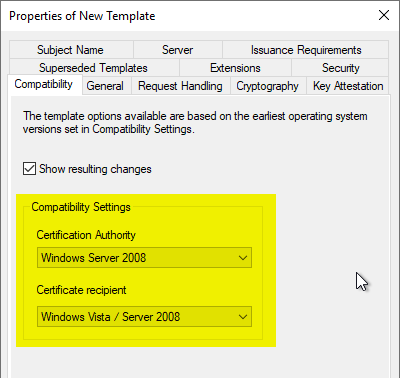
General" tab
A meaningful name is assigned in the "General" tab.
In the case of Remote Desktop certificate templates, it is essential to use the same value for the certificate template name and its display name, as it can be Otherwise, certificates may be applied for more than once..
Vulnerability scanners such as those from Qualys will report a discovery both if the certificate was not renewed one month before expiration and if the certificate is valid for more than one year. Since renewal via autoenrollment only occurs after 80% of the certificate validity has expiredIt therefore makes sense to set the certificate validity to a minimum of 6 months and a maximum of 12 months, and the time window for certificate renewal to at least 5 weeks.
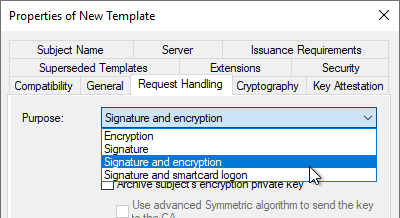
Request Handling" tab
In the "Request Handling" tab, the Purpose must be adapted to the key algorithm to be used. The background to this is that different requirements are placed on the "Key Usage" extension of the certificate depending on the key type (See RFC 5246 and RFC 4492).
| Key algorithm | Value |
|---|---|
| RSA | Signature and Encryption |
| ECDSA | Signature |
| ECDH | Signature and Encryption |
Cryptography" index card
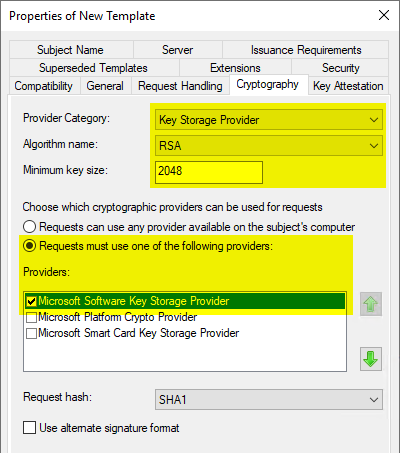
In the "Cryptography" tab, you can now select the "Key Storage Provider" category and the respective key algorithm.
The Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider should be selected as the provider if it is not intended to store the keys, for example, with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to protect
If a Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) is to be used, the "Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider"must be used. This only supports AT_KEYEXCHANGE, so the Purpose must be set to "Signature and Encryption" in the "Request Handling" tab. In principle, a key storage provider should be preferred if possible.
Here, however, there is the exception that the Active Directory Web Services (ADWS) already abort during certificate selection if even a single certificate in the computer certificate store does not use a CSP. Thus, it must be noted in this case that Remote Desktop certificates on domain controllers with activated ADWS also use a CSP.
The choice of provider only affects certificate requests that read the certificate template during the request (i.e., manual or automatic certificate requests via autoenrollment).
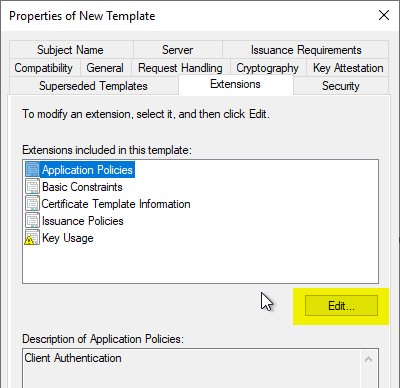
Extensions" tab
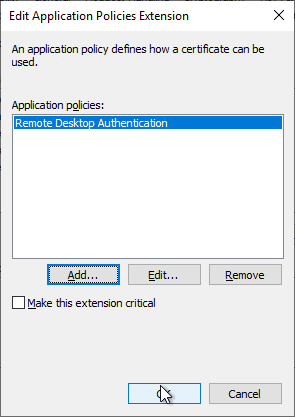
In the "Extensions" tab, the "Application Policies" are edited by clicking on "Edit...".
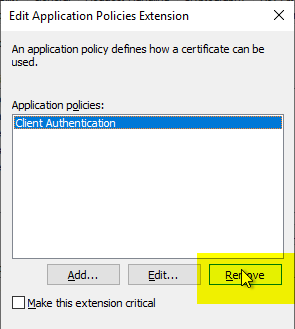
The existing "Client Authentication" EKU is removed by clicking on "Remove", as it is not required.
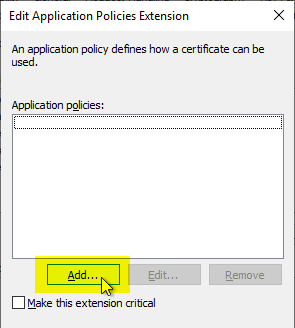
Subsequently, a new EKU is added with "Add...".
Since the Remote Desktop Authentication EKU is not defined in the delivery state of the Active Directory directory service, it must first be created by clicking on "New...".
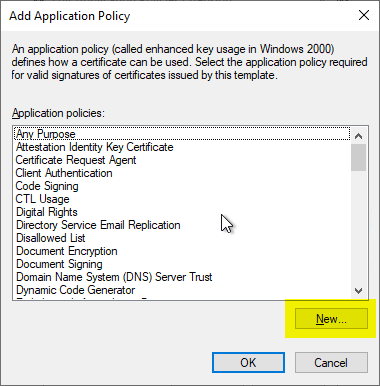
The predefined values in the following dialog are removed and the following are entered instead:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A free text field, but the text entered here will be displayed in the certificate dialog on every client in the network. Therefore, something meaningful like "Remote Desktop Authentication" should be entered. |
| Object identifier | Here exactly the following value must be entered: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.54.1.2 |
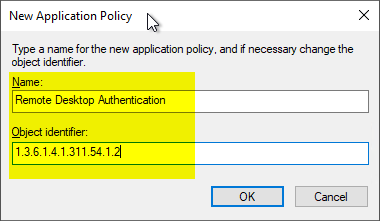
The newly defined EKU can now be selected and added by clicking on "OK".
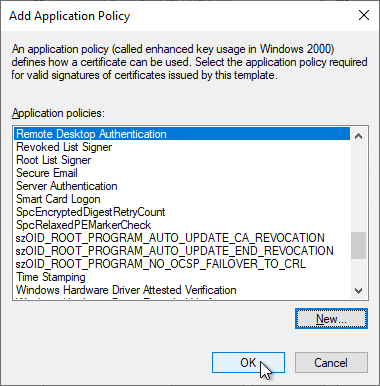
Click on "OK" to finish the configuration.
Security" tab
In the "Security" tab, the "Enroll" and "Autoenroll" permissions must be set for the participating computers.
If only "Enroll" is set, the machines will still apply for certificates, provided the corresponding group policy has been configured, as this corresponds to the fallback scenario. However, it is recommended to work with autoenrollment for better certificate management. Among other things, the fallback option does not archive expired certificates, which leads to the regular generation of the event with ID 64 of the source Microsoft-Windows-CertificateServicesClient-AutoEnrollment on the clients will lead.
Safety groups include, for example:
- Domain Computers (is already included in the list)
- Domain Controllers (must be added to the list)
If the Active Directory forest consists of several domains, all groups of the corresponding domains must be entered.
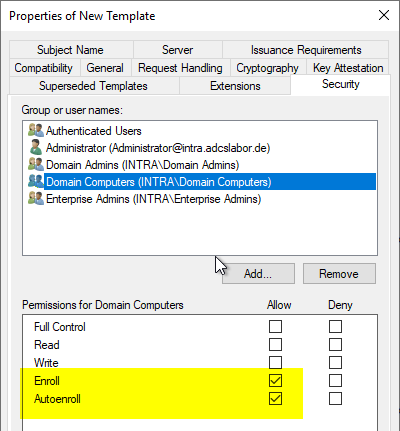
Technically, the "Enroll" permission is sufficient. However, it is strongly recommended that the "Autoenrollment" permission is also granted so that the certificates are distributed through this mechanism and used by the Remote Desktop session host. The client-side behavior is described in the article "Configuring a Group Policy (GPO) for Remote Desktop (RDP) Certificates" described.
Subject Name" tab
The option is described in the article "About the "Build this from Active Directory information" option for certificate templates" described in more detail.
The default settings of the "Workstation Authentication" certificate template can be used.
Result
The Remote Desktop Authentication Extended Key Usage is now displayed in the issued certificates because the corresponding OID object in the Public Key Services object of the forest is associated with this display name and is replicated by each participant in Active Directory.
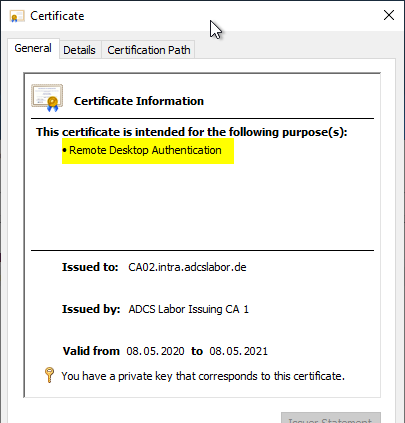
Next step: configure group policy
To ensure that the certificates are also used for the Remote Desktop session host, a corresponding group policy must now be configured. The procedure for this is described in the article "Configuring a Group Policy (GPO) for Remote Desktop (RDP) Certificates" described.
Related links:
- Basics of manual and automatic Certificate Enrollment via Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and Remote Procedure Call / Distributed Common Object Model (RPC/DCOM)
- Planning of certificate validity and renewal period of end entity certificates with autoenrollment
- Troubleshooting for automatic certificate request (autoenrollment) via RPC/DCOM
- Configuring a Group Policy (GPO) for Remote Desktop (RDP) Certificates
- Identify the active Remote Desktop (RDP) certificate
- Frequently Used Extended Key Usages and Issuance Policies
External sources
- Using certificates in Remote Desktop Services (Microsoft)
- Configuring Remote Desktop certificates (Microsoft, archive.org)
- Object IDs associated with Microsoft cryptography (Microsoft)
- Remote Desktop server certificates are renewed two times a day despite being valid for one year (Microsoft)
- Remote Desktop Services enrolling for TLS certificate from an Enterprise CA (Rob Greene, Microsoft)
8 thoughts on “Konfigurieren einer Zertifikatvorlage für Remotedesktop (RDP) Zertifikate”
Comments are closed.