The following is a description of the Enroll on Behalf Of function and how it differs from other methods of applying for certificates.
Functionality
Regular certificate request
A regular certificate request is usually in PKCS#10 format. The certificate request is signed with the private key belonging to the public key stored in the certificate request.

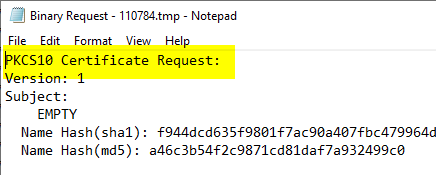
As the requester, the Active Directory identity of the account in the certificate authority database that sends the certificate request to the certificate authority is logged. The identity of the certificate corresponds to this account in the case of an online template; in the case of an offline template, the identity is taken from the certificate request.
Signed certificate request
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
For a signed certificate request, the PKCS#10 certificate request is converted to a Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS, RFC 5652, a further development of the PKCS#7 standard) or Certificate Management over CMS (CMC, RFC 5272) message.
The CMS message is signed with the private key of a certificate for a certificate enrollment agent.
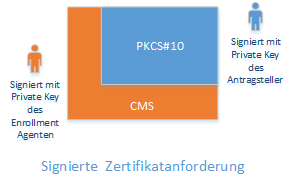
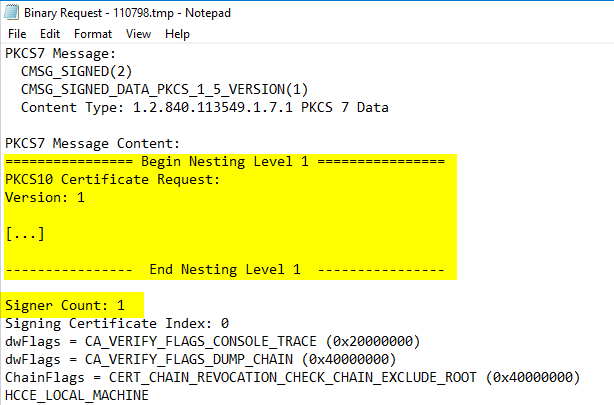
In this way, for example, an approval process can be implemented - a certificate registration agent can issue its approval after viewing the certificate request, and the certification authority can use the signature to ensure that the certificate request has been verified.
A popular example is the Network Device Registration Service (NDES)who signs incoming certificate requests with a corresponding certificate before forwarding them to the certification authority. The certification authority can then check the certificate request for the presence of this signature (which is not mentioned or required in Microsoft's instructions).
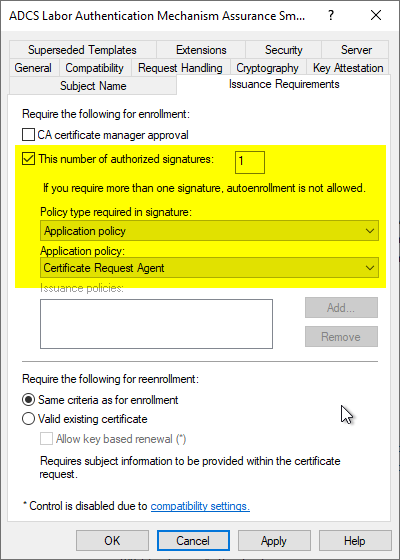
A corresponding configuration is made in the certificate template in the "Issuance Requirements" tab.
As the requester, the Active Directory identity of the account in the certificate authority database that sends the certificate request to the certificate authority is logged. The identity of the certificate corresponds to this account in the case of an online template; in the case of an offline template, the identity is taken from the certificate request.
Enroll on Behalf of (EOBO) Certificate Request
An Enroll on Behalf of certificate request also contains a RequesterName attribute, in which the identity of an account different from the requester is entered.
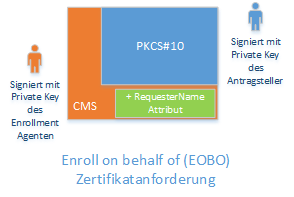
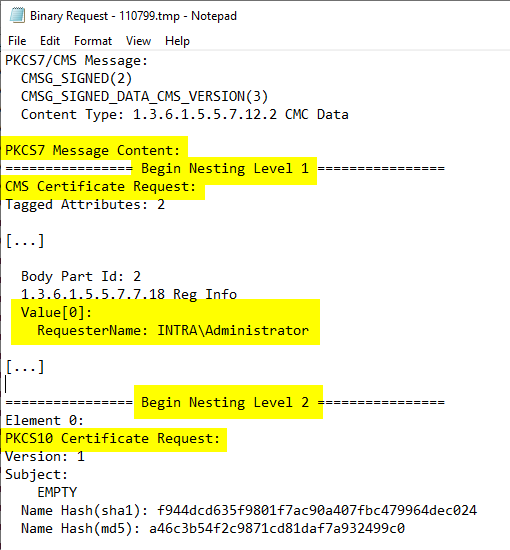
As the requester, the Active Directory identity of the account entered in the "RequesterName" attribute in the EOBO request is logged in the certification authority database. The identity of the certificate also corresponds to this account in the case of an online submission.
A typical application scenario would be the case of the employee ID card: this is issued by an employee of the HR department or building security with a certificate in the employee's name and then handed over to the employee, i.e. in such a case it is necessary for a third party classified as trustworthy to carry out the Certificate Enrollment for the employee.
Technical requirements for EOBO
- The certification authority that issued the enrollment agent certificate must be a member of NTAuthCertificates. For more information, see the article "Editing the NTAuthCertificates object in Active Directory„.
- The certificate template used for the request must require exactly one enrollment agent certificate. If none or more than one signature is configured as required, the certificate template will not be available for selection.
Certificate Enrollment procedure
The following describes the certificate request process from the perspective of the certificate enrollment agent. It is assumed that he already has a corresponding enrollment agent certificate at this point.
The agent opens the user certificate management console (cermgr.msc). Under Personal he right-clicks on Certificates and selects "All Tasks" - "Advancd Operations" - "Enroll On Behalf Of...".
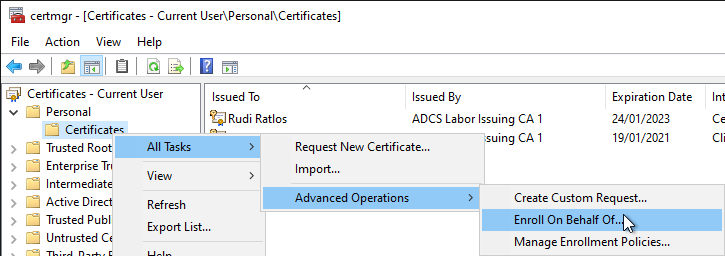
In the next dialog click on "Next" to continue...
In the next dialog (if available) the Certificate Enrollment Guideline (Enrollment Policy) and continue by clicking on "Next".
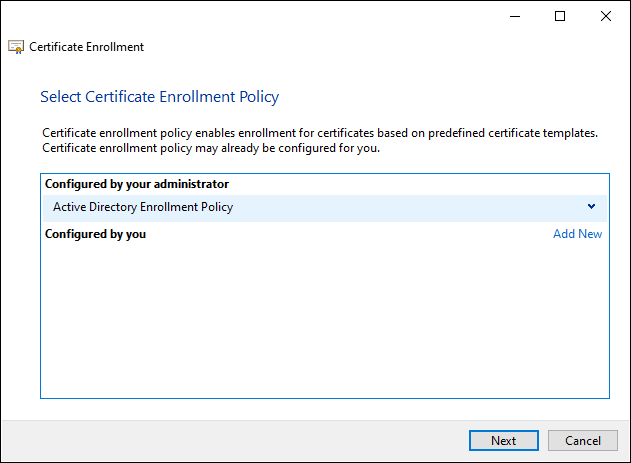
In the next dialog, the agent selects its certificate registration agent certificate.
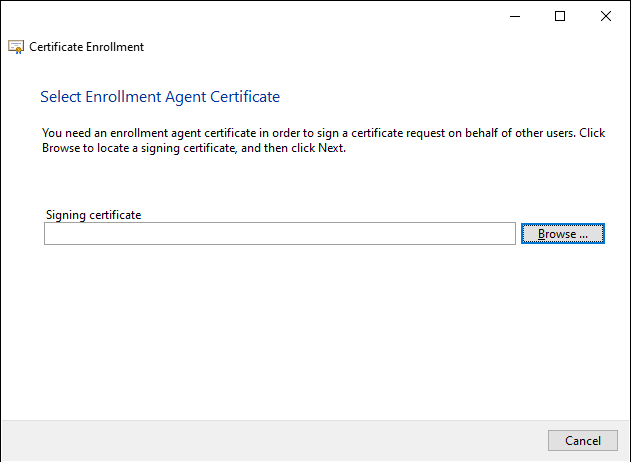
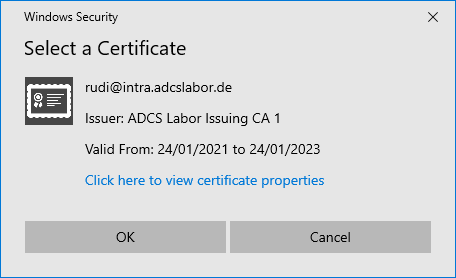
Then click on "Next" to continue...
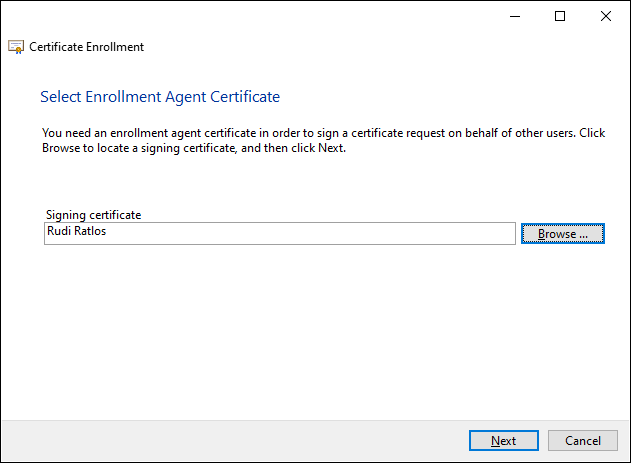
In the following dialog, the agent selects the certificate template to be used. Only those that require a signature by a certificate enrollment agent are displayed.
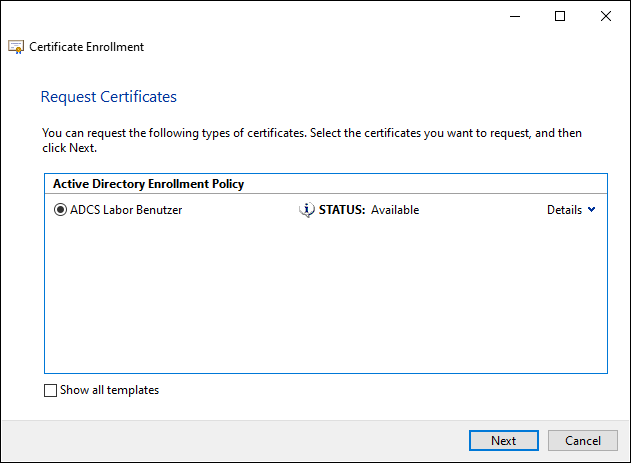
In the next dialog, the agent selects the user account for which he wants to request a certificate.
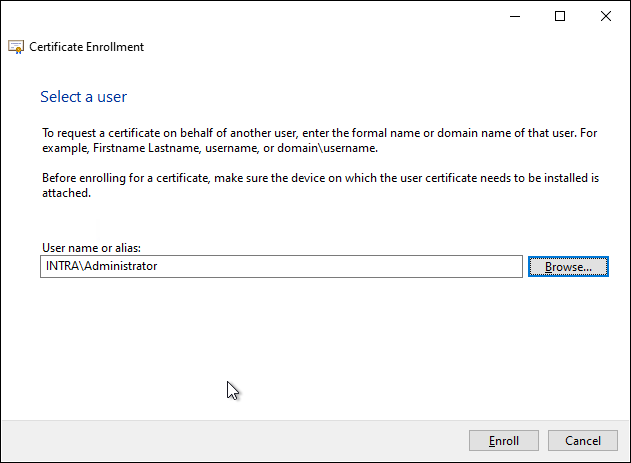
In the example, the domain administrator account was deliberately selected to demonstrate a fundamental problem with this mechanism: in the default setting, certificate enrollment agents can request certificates for any user in the Active Directory. This includes members of management as well as administrative accounts.
This makes it easy for a certificate enrollment agent to improperly assume other identities, which also can lead to a complete compromise of the Active Directory overall structure.
To limit this vector should be chosen very precisely, which certificate authorities are included in NTAuthCertificateswhich certificate authorities are allowed to issue certificates to certificate enrollment agents, and the Restricted Enrollment Agents feature should be used to restrict which agents are allowed to request certificates for which accounts on the relevant certificate authorities.
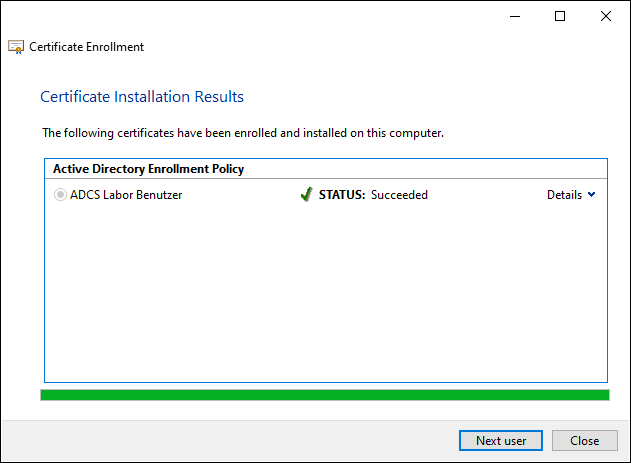
After clicking on "Next", the certificate for the user is requested. Afterwards, the process can be terminated or the next user can be selected.
Independent renewal of the certificate by the user
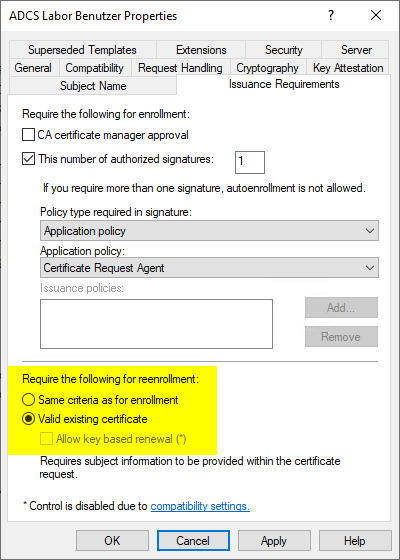
Please note that users can only renew a certificate requested via EOBO on their own if they are allowed to do so by the configuration of the certificate template. For this purpose, it must be configured under "Issuance Requirements" that users are automatically issued a certificate upon renewal if they already have a valid certificate from the same template.
Related links:
External sources
- [MS-CERSOD]: Example 6: Enroll on Behalf of Request and Renewal (Microsoft)
- [MS-WCCE]: Enroll on Behalf of Certificate Requests (Microsoft)
- RFC 5652 - Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS) (Internet Engineering Task Force)
9 thoughts on “Grundlagen: Enroll on Behalf of (EOBO)”
Comments are closed.