In principle, the RFC 5280 the use of arbitrary strings in the subject string of a certificate. Common fields in the standard are X.520 described. The Length restrictions are also recommended by the ITU-T. The abbreviations commonly used today are mainly taken from the RFC 4519.
However, Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services only allows certain RDNs by default.
The following Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs) are accepted by the Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) certificate authority by default:
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
| RDN | Description |
|---|---|
| emailAddress (E, EMAIL] Maximum 128 characters | The e-mail address of the certificate holder in the format name@domain.tld. For e-mail signature and encryption certificates, the identity is formed from this field. |
| commonName (CN) Maximum 64 characters | The common name. This can be used to map the identity of the certificate owner. However, for example with web server certificates, this should be done after RFC 2818 should be omitted and instead the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) should be used.. Free text. |
| organizationName (O) Maximum 64 characters | The name of the certificate holder's organization. Free text. |
| organizationalUnit (OU) Maximum 64 characters | The organizational unit (e.g. the specialist department) of the certificate holder. Free text. |
| localityName (L) Maximum 128 characters | The locality (for example, the city) of the certificate holder. Free text. |
| postalCode (POSTALCODE) | The zip code (e.g. "63486") of the certificate holder. Free text. |
| stateOrProvinceName (ST, S) Maximum 128 characters | The federal state (e.g. "Hessen") of the certificate holder. Free text. |
| countryName (C) Maximum 2 characters | A two-character country code according to ISO 3166 |
| domainComponent (DC) Maximum 128 characters | |
| unstructuredName (OID.1.2.840.113549.1.9.2) 1024 characters maximum | (not activated in the default setting) |
| unstructuredAddress (OID.1.2.840.113549.1.9.8) 1024 characters maximum | (not activated in the default setting) |
| deviceSerialNumber (SERIALNUMBER) 1024 characters maximum | (not activated in the default setting) |
| title (T) Maximum 64 characters | (not activated in the default setting) |
| givenName (G) Maximum 16 characters | (not activated in the default setting) |
| initials (I) Maximum 5 characters | (not activated in the default setting) |
| surname (SN) Maximum 40 characters | (not activated in the default setting) |
| streetAddress (STREET.) Maximum 40 characters | (not activated in the default setting) |
The limitation of the character lengths is based on the Recommendations of the ITU-T. It can be deactivated. See article "Certificate request fails with error message "Error Parsing Request The request subject name is invalid or too long. 0x80094001 (-2146877439 CERTSRV_E_BAD_REQUESTSUBJECT)".". In addition, the entire subject string is limited to 4096 characters and 4096 bytes for the ASN1-encoded variant of the subject string. The size limit for all certificate extensions (including the subject alternative name) is also 4096 bytes.
The setting can be checked with the following command line command on the certification authority:
certutil -v -getreg CA\SubjectTemplate
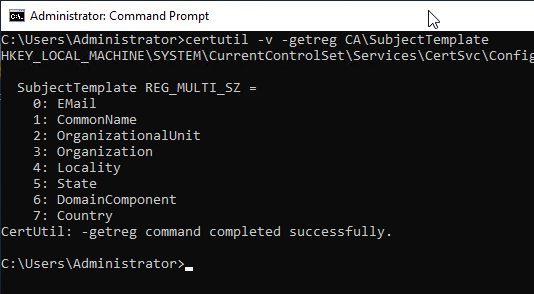
This setting is variable. For example, the installation of a NDES Servers add more RDNs.
By default, the certificate authority will enroll in issued certificates exactly according to the order defined here. Some applications have problems with this behavior. The order can be changed, or the Certification Authority be configured to accept the subject applied for without further examination.
Fine-grained control for manual certificate requests, which RDNs are allowed and which content is allowed can be achieved with the TameMyCerts Policy Module for Microsoft Certification Authority be made.
Related links:
- Installing the Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES) without Enterprise Administrator permissions
- Certificate request fails with error message "Error Parsing Request The request subject name is invalid or too long. 0x80094001 (-2146877439 CERTSRV_E_BAD_REQUESTSUBJECT)".
- Generating a RFC 2818 compliant certificate request for SSL certificates
External sources
- Distinguished Name Fields (Microsoft)
- Name Properties (Microsoft Learn)
- Managing Subject Relative Distinguished Names in the Certificate Subject (Microsoft)
- RFC 2818 - HTTP Over TLS (Internet Engineering Task Force)
12 thoughts on “Erlaubte Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs) im Subject Distinguished Name (DN) ausgestellter Zertifikate”
Comments are closed.