Since Windows NT 4.0, the Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) has been part of the CryptoAPI.
The purpose is that an application does not have to worry about the concrete implementation of key management, but can leave this to generic operating system interfaces. It is also intended to prevent cryptographic keys from being loaded into memory in the security context of the user/application being used (a fatal security incident based precisely on this problem was the Heartbleed incident).
For example, it makes no technical difference to the certification authority software how its private key is protected - whether in software or with a hardware security module (HSM), for example. The call of the private key is always identical for the certification authority.
With Windows Vista and the introduction of Cryptography Next Generation (CNG) as a replacement for CryptoAPI, Key Storage Providers (KSP) were introduced.
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
Introduction
Key storage provider benefits include:
- Key isolation. Keys can be used without leaving the KSP (important for use of keys stored in hardware).
- Auditability of key accesses (see event no. 5058 and 5059).
- Support for modern Algorithms like SHA2 and on elliptic curves based key.
Hardware manufacturers can develop their own CSP or KSP to provide access to their products. This is often the case with Hardware security modules (HSM, such as from SafeNet or Utimaco) or smartcards (from Gemalto or Yubico, for example).
Storage Locations
This refers to the storage locations of the private keys. Public keys are part of the associated certificates.
| Area | CryptoAPI / CSP | CNG / CSP |
|---|---|---|
| User | %AppData%\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\{User-SID} %AppData%\Microsoft\Crypto\DSA\{User-SID} | %AppData%\Microsoft\Crypto\Keys |
| Local system | %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\S-1-5-18 %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\DSA\S-1-5-18 | %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\SystemKeys |
| Local service | %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\S-1-5-19 %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\DSA\S-1-5-19 | %WinDir%\ServiceProfiles\LocalService |
| Network service | %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\S-1-5-20 %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\DSA\S-1-5-20 | %WinDir%\ServiceProfiles\NetworkService |
| All users | %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\MachineKeys %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\DSA\MachineKeys | %AllUsersProfile%\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\Keys |
Overview of the providers available in the Windows system
The following is an overview of KSP and CSP present on a modern Windows system.
Key Storage Provider
| Provider | Notes |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Passport Key Storage Provider | Used by Windows Hello for Business, among others. Can store keys transparently either in software or (if available) in a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). |
| Microsoft Platform Crypto Provider | Can key in a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) store. Does not support all CNG algorithms due to restrictions in the respective TPM standard. ECC key when requested via a certificate template only possible as of Windows 10 21H2 or Windows 11. |
| Microsoft Smart Card Key Storage Provider | Generic provider to store keys in a Smartcard to store. Supported by many smart card manufacturers. Support for certain algorithms depends on the smartcard used, e.g. the Microsoft virtual smartcard does not support ECC keys. |
| Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider | Generic provider to store keys in software. Supports all existing algorithms for certificates in the Windows ecosystem. Should be the minimum standard. |
Cryptographic Service Provider
Among the listed CSP, the following can be used to generate RSA keys up to 16384 bit key size:
- Microsoft Base Cryptographic Provider v1.0
- Microsoft Base Smart Card Crypto Provider (maximum 2048 bit key size)
- Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0
- Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider
- Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider (not for signature-only keys)
- Microsoft Strong Cryptographic Provider
| Provider | Notes |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Base Cryptographic Provider v1.0 | Should no longer be used if possible. |
| Microsoft Base DSS and Diffie-Hellman Cryptographic Provider | Cannot be used for the generation of RSA keys. Should no longer be used if possible. |
| Microsoft Base DSS Cryptographic Provider | Cannot be used for the generation of RSA keys. |
| Microsoft Base Smart Card Crypto Provider | Generic provider to store keys in a Smartcard to save. Maximum key length limited to 2048 bits. Should no longer be used if possible. |
| Microsoft DH SChannel Cryptographic Provider | Cannot be used for the generation of RSA keys. |
| Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0 | Should no longer be used if possible. |
| Microsoft Enhanced DSS and Diffie-Hellman Cryptographic Provider | Cannot be used for the generation of RSA keys. |
| Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider | Should no longer be used if possible. |
| Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider | Supports the SChannel Security Package and AES with up to 256 bit key length. Should therefore be used for TLS/SSL (e.g. Web server, Remote Desktop) can be used if no key storage provider is possible. Default setting for web server and CEP Encryption certificate templates. |
| Microsoft Strong Cryptographic Provider | Should no longer be used if possible. |
Use of Key Storage Providers
The usability of Key Storage Providers in a certificate template is released by setting the compatibility of the certification authority and the requesting clients to at least Windows Vista / Windows Server 2008. This raises the certificate template to version 3 and it can no longer be used by older operating systems.
See also the following articles:
- Description of certificate template generations
- How are the compatibility settings for certificate templates technically mapped?
Am I free to choose the provider when configuring my certificate template?
No, the use of the provider depends not only on its cryptographic capabilities but also on whether the application can use it. For example, operating systems prior to Windows Vista are not capable of using key storage providers. The Microsoft Platform Crypto Provider for example, does not support all algorithms.
Likewise, some applications still rely on the use of a CSP today. A prominent example is the Network Device Registration Service (NDES), as well as the associated connector for Microsoft Intune.
See also the following articles:
- List of use cases for certificates that require specific Cryptographic Service Providers (CSP) or Key Storage Providers (KSP).
- Which Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) should be used for the Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES)?
- Using custom Registration Authority (RA) certificate templates for the Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES).
Do I necessarily have to use a key storage provider?
It can be considered best practice to use a Key Storage Provider instead of a Cryptographic Service Provider wherever possible and to ensure that self-developed applications are compatible with them.
How can I view the providers installed on the system?
The providers present on a system can be listed with the following command:
certutil -csplist
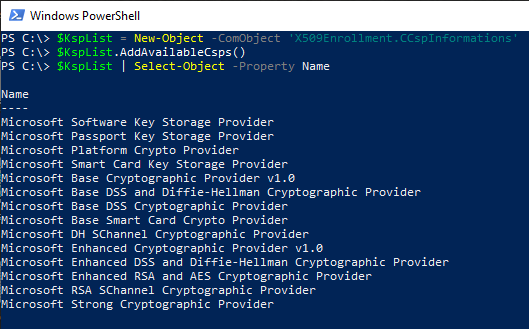
Via Windows PowerShell, listing is possible using the ICSPInformation COM object possible:
$KspList = New-Object -ComObject 'X509Enrollment.CCspInformations' $KspList.AddAvailableCsps() $KspList | Select-Object -Property Name
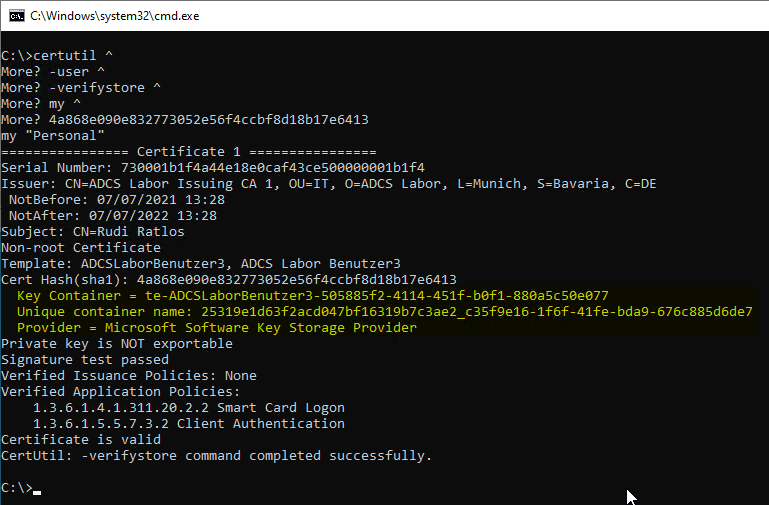
How can I find out which provider a particular certificate uses?
There is a "certutil" command for this. The corresponding certificate is identified by its SHA1 checksum (also called thumbprint).
For the computer certificate store:
certutil -verifystore my {Thumbprint}
For the certificate store of the currently logged in user:
certutil -user -verifystore my {Thumbprint}
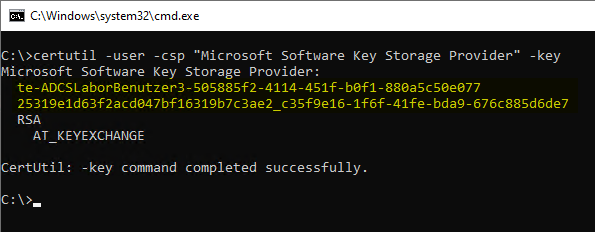
How can I list the keys protected by a particular provider?
There is also a "certutil" command for this:
For the computer certificate store:
certutil -csp "{CSPName}" -key
For the certificate store of the currently logged in user:
certutil -user -csp "{CSPName}" -key
Related links:
- Basics: key algorithms, signature algorithms and signature hash algorithms
- Basics: Elliptic curves with regard to their use in the public key infrastructure
External sources
- Cryptography Next Generation (Microsoft Corporation)
- CNG Key Storage Providers (Microsoft Corporation)
- CryptoAPI Cryptographic Service Providers (Microsoft Corporation)
- certutil (Microsoft Coropration)
- Difference between Cryptographic Service Providers (Microsoft Strong vs RSA SChannel) (Microsoft TechNet Forums)
- Understanding Microsoft Cryptographic Service Providers (PKI Solutions, Inc.)
- Checking Windows Hello Key Storage: TPM or Software? (Helge Klein)
- Certificate enrollment: Crypto API, CNG, and other Windows APIs (Johannes Passing)
- How to keep a secret in Windows (Ryan Hurst)
26 thoughts on “Grundlagen: Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) und Key Storage Provider (KSP)”
Comments are closed.