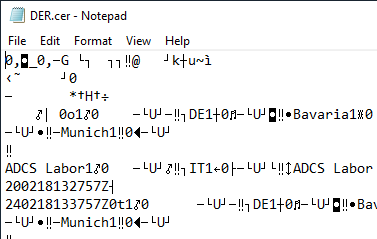
X.509 certificates are always encoded in the Distinguished Encoding Rules (DER) format. This is a binary, machine-readable format.
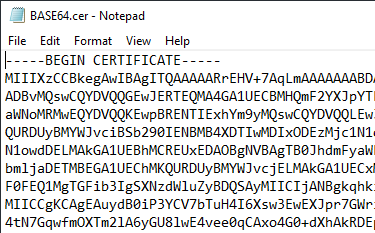
DER-encoded certificates can, however, also be converted into a text-based format using the BASE64 process so that they can be transmitted in an e-mail body, for example. BASE64 encloses the DER-encoded format, i.e. the certificate is and remains DER-encoded in any case.
In practice, files with different file extensions are used for certificates. The most common ones are briefly described below.
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem, has already proven itself in countless companies around the world and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge. Professional maintenance is also offered.
| File extension | Content |
|---|---|
| .the | Binary (DER encoded) certificate. |
| .pem | Certificate in text format (BASE64 encoded DER). |
| .cer, .crt | Can be present as DER or as BASE64 encoded DER. |
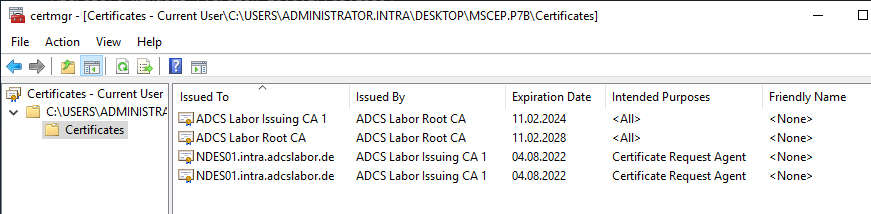
| .p7b | PKCS#7 container, which can contain multiple certificates that can be both DER or BASE64-encoded DER. Thus, for example, an entire certificate chain can be transmitted within only one file (for example, in the GetCACert operation in SCEP protocol). |
This leaves three options for packaging a certificate (DER, BASE64 or PKCS#7). Exactly these three options are also offered by the certificate export dialog.
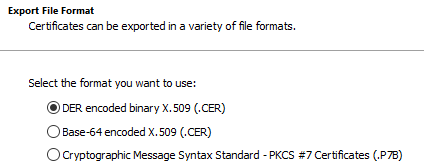
Examples
Related links:
External sources
- A Layman's Guide to a Subset of ASN.1, BER, and DER (RSA Laboratories)
- RFC 7468 - Textual Encodings of PKIX, PKCS, and CMS Structures (Internet Engineering Task Force)
- What is PEM Format? (DigiCert)
- PKCS 7 - Wikipedia
- BASE64 - Wikipedia
One thought on “Beschreibung der verschiedenen Zertifikat-Formate”
Comments are closed.