When working with Certificate Enrollment Web Services and manually entering certificate enrollment policies on client computers, one encounters the phenomenon that there is no way to edit or delete them in the Certificate Management Console.
Continue reading „Löschen einer manuell konfigurierten Zertifikatbeantragungs-Richtlinie (Enrollment Policy)“Month: April 2020
The creation of a certificate enrollment policy for the Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service (CEP) fails with the error message "This ID conflicts with an existing ID."
Assume the following scenario:
- A Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service (CEP) is implemented in the network.
- An enrollment policy is configured.
- Testing the connection fails with the following error message:
The URI entered above has ID: "{{GUID}}". This ID conflicts with an existing ID.
Continue reading „Die Erstellung einer Zertifikatregistrierungsrichtlinie (Enrollment Policy) für den Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service (CEP) schlägt fehl mit der Fehlermeldung „This ID conflicts with an existing ID.”“ Basics of certificate application via Certificate Enrollment Web Services (CEP, CES) with the MS-XCEP and MS-WSTEP protocols
With Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7, a new functionality for certificate enrollment has been introduced: The Certificate Enrollment Web Services, which are mapped by two server roles:
- Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service (CEP)
- Certificate Enrollment Web Services (CES)
The following is a description of the background to these roles, how they work, and the possible deployment scenarios.
Continue reading „Grundlagen Zertifikatbeantragung über Certificate Enrollment Web Services (CEP, CES) mit den Protokollen MS-XCEP und MS-WSTEP“Basics of manual and automatic certificate requests via Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and Remote Procedure Call / Distributed Common Object Model (RPC/DCOM) with the MS-WCCE protocol
The following describes the process that runs in the background when certificates are requested manually or automatically in order to achieve the highest possible level of automation.
Continue reading „Grundlagen manuelle und automatische Zertifikatbeantragung über Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) und Remote Procedure Call / Distributed Common Object Model (RPC/DCOM) mit dem MS-WCCE Protokoll“Manually running the autoenrollment process
By default, all domain members automatically replicate the Public Key Services object he Active Directory forest through the autoenrollment process. The triggers for this are:
- When the user logs in (for computers, when the computer account logs in, i.e. at system startup).
- By timer every 8 hours.
- When updating group policies, assuming there has been a change.
If you do not want to wait for the autoenrollment to be triggered automatically, you can start it manually. The different ways to run the autoenrollment process are described below.
Continue reading „Manuelles Ausführen des Autoenrollment Prozesses“Associate a universal security group with an Object Identifier (OID) in the Active Directory directory service (Authentication Mechanism Assurance).
Authentication Mechanism Assurance (AMA) provides the ability to tie membership in a security group to enrollment with a smart card certificate containing a specific Object Identifier (OID).
If the user does not log in with the smartcard certificate, but with user name and password, he is also not a member of the security group.
The following describes how to establish the connection between the certificate and the security group.
Continue reading „Eine universelle Sicherheitsgruppe mit einem Object Identifier (OID) im Active Directory Verzeichnisdienst verbinden (Authentication Mechanism Assurance)“Configuring a Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Certificate Template for Web Server
Below is a guide to configuring a web server template with recommended settings.
Continue reading „Konfigurieren einer Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Zertifikatvorlage für Web Server“Allowed Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs) in the Subject of Issued Certificates
In principle, the RFC 5280 the use of arbitrary strings in the subject string of a certificate. Common fields in the standard are X.520 described. The Length restrictions are also recommended by the ITU-T. The abbreviations commonly used today are mainly taken from the RFC 4519.
However, Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services only allows certain RDNs by default.
The following Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs) are accepted by the Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) certificate authority by default:
Continue reading „Erlaubte Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs) im Subject Distinguished Name (DN) ausgestellter Zertifikate“Inspect a certificate request (CSR)
Often, before submitting a certificate request to a certification authority - or before issuing the certificate - you want to verify that it contains the desired values.
The following describes how to achieve this.
Continue reading „Eine Zertifikatanforderung (CSR) inspizieren“Subsequently change the Subject Distinguished Name (DN) of a certificate request (CSR)
Sometimes it is necessary to change the Subject Distinguished Name (also called Subject, Subject DN, Applicant or Subject) of a certificate request before issuing the certificate.
Under certain circumstances, this is certainly possible, as described below.
Continue reading „Den Subject Distinguished Name (DN) einer Zertifikatanforderung (CSR) nachträglich verändern“Configuring a Certificate Template for Authentication Mechanism Assurance (AMA)
Authentication Mechanism Assurance (AMA) provides the ability to tie membership in a security group to enrollment with a smart card certificate containing a specific Object Identifier (OID).
If the user does not log in with the smartcard certificate, but with user name and password, he is also not a member of the security group.
The following describes how to generate a certificate template for use with Authentication Mechanism Assurance.
Continue reading „Konfigurieren einer Zertifikatvorlage für Authentication Mechanism Assurance (AMA)“Include the wildcard issuance policy (All Issuance Policies) in a certification authority certificate
If you install an issuing CA and do not explicitly request an issuance policy, the resulting CA certificate will not contain an issuance policy.
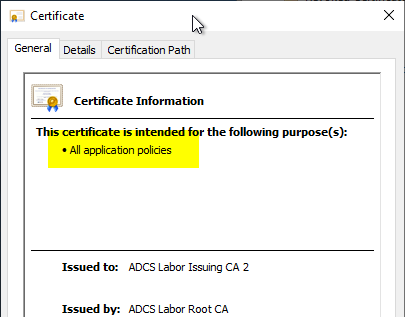
If you want to include the wildcard issuance policy (All Issuance Policies) in the certification authority certificate, you must proceed as follows:
Continue reading „Die Wildcard Ausstellungsrichtlinie (All Issuance Policies) in ein Zertifizierungsstellen-Zertifikat aufnehmen“Include the issuance policies for Trusted Platform (TPM) Key Attestation in a certification authority certificate.
If you install an issuing CA and do not explicitly request an issuance policy, the resulting CA certificate does not contain an issuance policy.

If you want to include the issuance policies for Trusted Platform (TPM) Key Attestation in the certification authority certificate, you must proceed as follows.
Continue reading „Die Ausstellungsrichtlinien (Issuance Policies) für Trusted Platform (TPM) Key Attestation in ein Zertifizierungsstellen-Zertifikat aufnehmen“Determine and export a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Endorsement Certificate
If you want to use the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) key attestation, you have the option of attesting the TPM via the endorsement certificate (EkCert), among other things. The following describes how to obtain this information.
Continue reading „Ermitteln und Exportieren eines Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Endorsement Zertifikats“Determine the checksum (hash) of a Trusted Platform (TPM) Endorsement Key
If you want to use the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) key attestation, you have the option of attesting the TPM via the endorsement key (EkPub), among other things. The following describes how to obtain this information.
Continue reading „Die Prüfsumme (Hash) eines Trusted Platform (TPM) Endorsement Key ermitteln“